From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) began on January 24, 1848, when gold was discovered at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. News of the discovery soon spread, resulting in some 300,000 men, women, and children coming to California from the rest of the United States and abroad.
These early gold-seekers, called "forty-niners," traveled to California by sailing ship and in covered wagons across the continent, often facing substantial hardships on the trip. While most of the newly-arrived were Americans, the Gold Rush attracted tens of thousands from Latin America, Europe, Australia and Asia. At first, the prospectors retrieved the gold from streams and riverbeds using simple techniques, such as panning, and later developed more sophisticated methods of gold recovery that were adopted around the world. Gold, worth billions of today's dollars was recovered, leading to great wealth for a few; many, however, returned home with little more than they started with.
The effects of the Gold Rush were substantial. San Francisco grew from a tiny hamlet of tents to a boomtown, and roads, churches, schools and other towns were built. A system of laws and a government were created, leading to the admission of California as a state in 1850. A unique social structure evolved. New methods of transportation developed as steamships came into regular service and railroads were built. Agriculture, California's first big attraction, developed on a wide scale throughout the state as gold mines produced less. However, the Gold Rush also had negative effects: Native Americans were attacked and pushed off traditional lands, race and ethnic tensions formed, and gold mining caused environmental harm.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
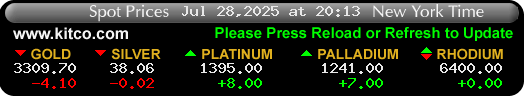
Latest gold Prices